Unwelcome Invaders: A Comprehensive Guide to Expelling Parasites, Worms, and Harmful Bacteria from Your Body
Naturopathic Doctor, Clinical Herbalist, Iridologist, Author and Lecturer
The idea of harboring parasites, worms, or protozoa within the human body can feel unsettling. Having lived in Southeast Asia, I experienced firsthand how easy it is to contract infections like giardia parasites, which led to severe weight loss and fatigue. Parasites are opportunistic organisms that drain our nutrition, disturb gut health, and weaken immunity.
Research suggests that one-third of the global population may have a parasitic infection, ranging from intestinal worms to bacterial overgrowth. This makes parasite cleansing and natural detox remedies essential for overall health.
How Do You Get Parasites?
You may unknowingly host intestinal parasites through:
- Eating undercooked meat (especially pork and fish)
- Drinking unfiltered water
- Traveling to developing countries
- Playing with pets or children who carry worms
- Poor hygiene and handwashing habits
- Diets high in sugar, processed foods, and dairy
Low stomach acid, weak gut immunity, and frequent antibiotic use can make the body more susceptible to parasitic infections.
Common Symptoms of Parasites
Wondering if you might have a parasite? Common parasite symptoms include:
- Digestive problems: diarrhea, constipation, bloating, gas
- Constant hunger, food cravings, or appetite loss
- Fatigue and weakened immunity
- Iron deficiency and anemia
- Muscle and joint pain
- Skin issues: rashes, itching, hives, brittle hair
- Mental health effects: anxiety, depression, brain fog
- Sleep disturbances (teeth grinding, restlessness, waking often)
Parasites rob the body of nutrients, leading to malnutrition, weight changes, and gut imbalance.

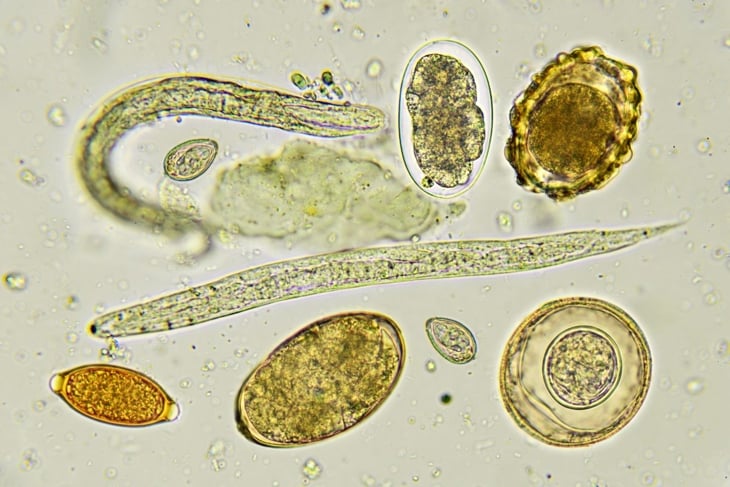
Types of Parasites in Humans
Several parasites affect humans, including:
- Hookworms – feed on blood, cause anemia
- Roundworms – spread easily from pets and soil
- Flukes – intestinal and liver flukes from undercooked fish or contaminated water
- Protozoa – Giardia, Blastocystis hominis, Entamoeba, Cryptosporidium
- Tapeworms – beef, pork, and fish tapeworms that can migrate to muscles and the brain
- Threadworms/Pinworms – common in children, cause anal itching
Knowing which parasite infection, you may have is key to proper treatment.
Natural Remedies to Kill Parasites
The best natural anti-parasitic foods and herbs include:
- Raw garlic – powerful antimicrobial and antiparasitic
- Pumpkin seeds – paralyze intestinal worms
- Papaya seeds – traditional remedy for intestinal worms
- Pineapple & papaya fruit – reduce gut inflammation
- Ginger – boosts stomach acid and fights harmful bacteria
- Coconut oil & coconut meat – antibacterial and supports digestion
- Turmeric – anti-inflammatory, supports liver and gut health
- Cloves & oregano – potent antiparasitic spices

Step 1: Cleanse and Eliminate Parasites
After decades in practice, I’ve found that many parasite cleanses are ineffective against stubborn parasites like Blastocystis. My go-to herbal allies include:
- Berberine herbs (barberry, Oregon grape, goldenseal)
- Oregano oil, garlic, myrrh, thyme, anise
- Black walnut & green walnut hulls
- Sweet wormwood (Artemisia annua)
- Neem & grapefruit seed extract (GSE)
- Medicinal mushrooms – Reishi, Chaga, Maitake, Cordyceps
These herbs and extracts act as natural parasite killers, supporting both detox and immune defense.
Step 2: Rebuild Gut Health After Parasite Cleanse
Once parasites are eliminated, rebuilding the gut microbiome is vital. Strengthen digestion and prevent reinfection by:
- Eating fermented foods: kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut
- Taking prebiotics and probiotics
- Supporting stomach acid and enzymes with herbs and bitters
- Healing the gut lining for long-term digestive health
|
Wholistic House Parasite Support My recommended anti-parasitic supplement pack includes:
|
Parasites and worms are far more common than most realize. By cleansing regularly, eating antiparasitic foods, and restoring gut balance, you can protect your health and live parasite-free.
In love, health and super clean bowels,

Referenced products






Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
All comments are moderated before being published.